Global warming is caused by ozone depletion, not greenhouse gases
| 06-12-2014 15:29 | |
| peterlward★☆☆☆☆ (69) |
Abraham3, Your comments sent last night were well researched and thought out and we seemed to have a reasonable discussion going. Then you saw my comments to Surface Detail and took them personally, going ballistic. You have done some research. It is not clear that Surface Detail has done as much and I was speaking to him. If you are unwilling to seriously consider the likelihood that waves cannot propagate in space and that energy of EMR in space equals hv, then there is no sense in discussing anything else. |
| 06-12-2014 21:29 | |
| Abraham3 (256) |
I have no problem with Planck's relation. I have considered your contention that EMR in a vacuum has no wavelength but I find the idea unacceptable for a number of reasons, all of which I've stated. I would like to continue this discussion if for no reason than to come to a mutual understanding of our separate positions. But a discussion takes two. If you wish to end the conversation, consider it done. |
| 07-12-2014 03:34 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
Peter, have a look at this graph of central England temperatures and note what it was during in 1783 at the time of the eruption of Laki-Grímsvötn volcano, in Iceland. That eruption emitted so much sulphur dioxide (120 million tons of sulphur dioxide) that it equaled the eruption of a Mt. Pinatubo eruption every three days. And yet, as volcanologists have been saying for many years, the result was, not warming, but cooling. Nowhere in the 3-5 years after that eruption do we see warming that you claim occurs from SO2 emission from volcanoes. How do you account for this discrepancy in your hypothesis?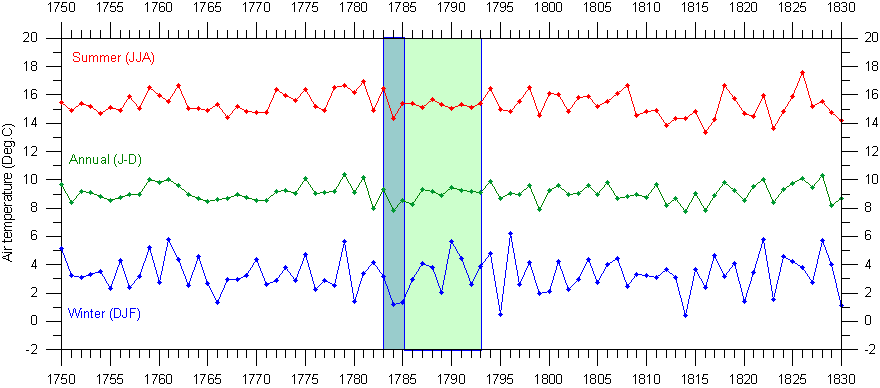 http://www.climate4you.com/ClimateAndHistory%201700-1799.htm#1783-1784: The Laki eruption in Iceland https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=anCsgtDPy64 Edited on 07-12-2014 04:05 |
| 07-12-2014 06:31 | |
| peterlward★☆☆☆☆ (69) |
Abraham, Home finally after a week on the road. The issue is: exactly how does thermal energy (EMR) travel through the vacuum of space. What is the "microphysics"? Exactly what is happening described physically, not mathematically? We understand elastic wave propagation in matter quite well and compressional waves in water and the atmosphere. Waves and frequencies in matter interact with each other. Frequencies and amplitudes are attenuated with distance. Energy is proportional to the square of the amplitude. We can see and measure frequency and see and measure wavelength. Wave equations explain observations quite well. For EMR in space, we observe and measure frequency and brightness that I claim is amplitude of the oscillations on the radiating surface. Frequencies do not interact and are not attenuated with distance. Amplitude is proportional to the inverse square of distance and this makes sense because as EMR radiates, the same amplitude is spread out over an area that increases with the square. We observe that energy of EMR is proportional to frequency as proposed by Planck. We observe that when matter is heated, the frequency and the amplitude of oscillations of all the bonds that hold matter together increase. We observe the volume increases, which is the result of the amplitudes increasing. Thermal energy in matter is frequency and the frequencies, amplitudes, and volume go to zero as temperatures go to absolute zero. It is not clear that thermal energy, heat, in matter, is wavelike. But in thermodynamics we primarily study equilibrium states and waves, if they were present, would have to die out before thermal equilibrium could exist. So what physics would you propose explains EMR in space as having wavelength? What observations, measurements demonstrate the presence of wavelength in space, away from any matter? I assume we agree that when EMR interacts with matter, we do see effects that can be explained in terms of wavelength and that suggest wavelength occurs in matter. Surface Detail, What temperature data are these? Where and how were they measured? Laki was basically an effusive eruption, one of the largest in historic time, but there were ten eruptive phases in June through October. Some SO2 did get lofted to the stratosphere and early cooling was observed to the east over Scandinavia. But major amounts of SO2 was taken by the jet stream to the southeast, causing acid rain sufficient to destroy leases from the British Isles to Finland, to Italy. Ultimately perhaps 50,000 people died, some from respiratory problems, most from famine. Warming of more than 3oC was measured in Europe, especially in the Netherlands and surrounding countries. There is a great deal of information available on Laki and I have spent time walking among the vents. Please note that in my 2009 paper, I suggested that SO2 might cause the warming. I now believe that SO2 and sulfate are the footprints of volcanism and that volcanism causes ozone depletion that causes the warming. If substantial aerosols are formed in the lower stratosphere, then these cause net cooling. I am not aware of reliable global temperature data from this time and would like to find out more about the data you plot. |
| 07-12-2014 07:56 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
So what physics would you propose explains EMR in space as having wavelength? What observations, measurements demonstrate the presence of wavelength in space, away from any matter? I assume we agree that when EMR interacts with matter, we do see effects that can be explained in terms of wavelength and that suggest wavelength occurs in matter. Well, first of all we all recognize that EMR consists of a wide range of wavelengths from infrared to microwaves. Right? So, from an observational standpoint, when we look at EMR in outer space, particularly from space where there is little to no atmosphere (i.e., the Hubble space telescope), as well as on the ground, as a whole, we see the entire spectrum of wavelengths. Hubble can image from near infrared to UV. These are wavelengths that are being measured. We know this because we are using filters that only allow specific wavelengths (such as hydrogen alpha) to pass through to the CCD sensor. In fact, the Spitzer Space telescope was sent to space because terrestrial infrared wavelengths (particularly those scattered in the atmosphere) interfere with astronomical observations, and so to see the wavelengths emitted by objects that astronomers were interested in, they built and launched Spitzer into outer space. If wavelengths are not propagated in space, they would have wasted a lot of taxpayer dollars. Radio telescopes can measure an abundance of different radio wavelengths. The Chandra space telescope measures x-ray wavelengths very precisely. So the question that comes to mind is with these facts at hand, how can you so readily ignore/dismiss what every other scientist recognizes as scientific fact? That EMR wavelengths propagate so readily through outer space. What fact do you have at your command that all these other scientists don't possess? Edited on 07-12-2014 08:06 |
| 07-12-2014 08:05 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
Surface Detail, Peter, I believe you were responding to my post so I will answer here. There temperature data I posted were measured and compiled in England. Please refer to the link I provided. You say that warming occurred in Europe, in the Netherlands, you say. I have seen no temperature data that corroborates your claim. In fact, all the historical data I've seen make it clear that Europe suffered from very low temperatures after the eruption, and for at least a couple of years afterwards. If there is not, as you say, any reliable temperature database available, how can you claim that the temperature increased by as much as 3 degrees C? Considering the fact that Scandinavia reported the worst winter in 250 years in 1783, as did Britain, I find your claim to be dubious. You keep asking us for data, so I am asking for specific source data that corroborates your claim, not simply a re-statement of the claim. |
| 07-12-2014 19:43 | |
| peterlward★☆☆☆☆ (69) |
Surface Detail, The climate4you.com article is relatively well written for a general audience but is thin on science. The best scientific summary is Thordarson, T., and S. Self (2003), Atmospheric and environmental effects of the 1783–1784 Laki eruption: A review and reassessment, J. Geophys. Res., 108(D1), 4011. Figure 8 shows "Deviation of the 1783 July surface temperatures from the 1768–1798 mean." There are many other papers by Thordarson plus his Thesis that give much more detail plus many papers by other authors looking at the climate effects of the Laki eruption. I have 6 pages of notes detailing a timeline based on 9 of these papers. The temperature data from central England certainly do not represent mean surface global temperatures. There is much work to be done on the Laki eruption and its climate effects. It is complicated by the observation of sulfuric acid aerosols, so it is not a simple effusive eruption. The most noteworthy observation, even made by Benjamin Franklin, was the dry fog blanketing Europe that appears to have been primarily SO2. As for wavelength, we commonly refer to EMR in space as having a wavelength. But my point is that we do not observed the wavelength directly. We observe frequency and calculate wavelength as the velocity of light divided by the frequency. Wavelength in space is a mathematical quantity, not a physical property of EMR. There is no way for wavelength to physically exist in space. The physical properties of EMR in space are frequency and some form of amount, amplitude, brightness, spectral radiance, all of which get back to the amplitude of the oscillation on the surface of matter issuing the radiation. |
| 08-12-2014 00:49 | |
| Abraham3 (256) |
Why do you believe there is no way for an EMR wavelength to exist in a vacuum? Is atmosphere required for the existence of an electric or magnetic field? And then there's the point that there's really no such thing as a vacuum - just thinner and thinner gas densities. At what point do you believe EMR waves become impossible? Edited on 08-12-2014 00:49 |
| 08-12-2014 01:57 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
peterlward wrote: Why do you keep calling me Surface Detail? I am orogenicman. Okay, I read Thordason and Self, and it clearly shows in Figure 9 a reconstruction of global mean temperatures for a 31 year period centered on the time of the Laki eruption. From that graph, it is clear that after the eruption temperatures worldwide experienced a significant drop as a result of the eruption. In fact, according to their graph, temperatures didn't rebound to pre-eruption levels until 1791 at the earliest. The data showing a heat wave in northwest Europe in July 1793 is not clearly connected to the eruption, and was likely simply a heat wave and nothing more since it began before the eruption impacted the region. Particularly when you consider that in other regions affected by the ash and gas, temperatures were near to below normal. As for your claim that wavelength is not directly observed in outer space, you cannot be more mistaken. As I've already pointed out, the Hubble Space telescope, and every other space telescope ever placed into outer space, DIRECTLY measures the wavelength of emission. They do it by two methods; specialized filters that only allowed passthrough of specific wavelengths of light (i.e., hydrogen alpha, Hydrogen beta, OIII, SII, and ionized nitrogen - I own a set of these myself), and via spectroscopy. http://www.spacetelescope.org/about/general/instruments/stis/ The Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) is a versatile "combi-instrument" taking advantage of modern technologies. It combines a camera with a spectrograph, and covers a wide range of wavelengths from the near-infrared region into the ultraviolet. Face it, Peter, you are mistaken when you say that EMR wavelengths cannot be measured directly. They have been and are being measured. I have measured them directly myself. I have photographed them as well. If it were not possible for light in the various wavelengths of EMR to travel through outer space, the entire scientific field of astronomy would not exist. 'The difference between a Miracle and a Fact is exactly the difference between a mermaid and seal. It could not be expressed better.' -- Samuel "Mark Twain" Clemens Edited on 08-12-2014 02:15 |
| 08-12-2014 05:04 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
Also note on page 18 of Thordason and Self:The July anomaly is strongest in western Europe and declines gradually with increasing distance from Laki, which can be taken as support for the above hypothesis. However, it is challenged by the fact that at the same time cool conditions prevailed in Iceland and Faeroe Islands [Ho´ lm, 1784; Jo´nsson and Pa´ lsdo´ ttir, 1992; Lievog, 1783], regions which were consistently exposed to the gaseous emissions from Laki. Also, unusually warm temperatures are not seen in the August temperature records from the same European stations although the sulfuric haze was still present in abundance [Thordarson, 1995]. An alternative explanation is that the warm spell may have been caused by somewhat unusual developments in the atmospheric circulation pattern over Europe in July 1783. Edited on 08-12-2014 05:04 |
| 08-12-2014 05:23 | |
| peterlward★☆☆☆☆ (69) |
Sorry but these instruments do not measure wavelength. They measure frequency. You basically count the number of zero crossings or peaks within a unit of time. This gives you frequency which you can turn into wavelength inside the machine or outside of it using the velocity of light. It is basic physics that waves do not and cannot travel through the vacuum of space. The frequencies making up waves interact with each other and change with distance. The frequencies making up EMR do not interact with each other and frequency is not changed over galactic distances except for Dopplar effects. These are very clear physical observations. |
| 08-12-2014 07:26 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
peterlward wrote: Narrow band filters do one thing, and one thing only. They allow only the wavelength for which they are made pass through the filter into a camera lens and/or a telescope/camera. That wavelength can and is measured on Earth, and what is measured in outer space is exactly the same. You can verify this yourself by measuring the wavelength of a hydrogen flame with a spectrometer, and then measuring sunlight. At the exact same wavelength you will find the hydrogen alpha spectrum. There is no variation in this, no missing spectrum. They are exactly the same. Unlike sound waves, light waves are not vibrations. They need no medium to pass through. In fact, light travels faster in a vacuum than it does through a medium. Light is an electromagnetic wave - a combination of electrical and magnetic fields - which does not require the presence of a gas or other medium to propagate. It is carried around in fundamental pieces as photons. These display the "wave-particle duality" behavior, which means they behave as a wave or as a particle. In the case of light passing through a vacuum, the photon behaves as a particle and moves freely through the empty vacuum. The image below is of a nebula taken with a hydrogen alpha filter. Everything you see in this image is emitting photons at the wavelength of hydrogen alpha because it is composed of ionized hydrogen gas. It is the wavelength, not the frequency. You cannot measure frequency with a narrowband filter because it is designed to allow only a specific wavelength to pass though. In this case, the wavelength is exactly 656.28 nm  'The difference between a Miracle and a Fact is exactly the difference between a mermaid and seal. It could not be expressed better.' -- Samuel "Mark Twain" Clemens Edited on 08-12-2014 07:29 |
| 08-12-2014 07:53 | |
| peterlward★☆☆☆☆ (69) |
A filter is matter and light interacts with matter in a wavelike manner. Please explain what a wave of light IS physically in space. Not an equation. What is physically there and how it propagates. What moves? How does it propagate? How do the waves interact with other waves of light? Waves are a property of matter. Waves in matter have very different properties from EMR. |
| 08-12-2014 08:13 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
peterlward wrote: http://www.chem1.com/acad/webtext/atoms/atpt-2.html#LRAD Light is electromagnetic radiation, your EMR. It is composed of a particle and a wave. What is "waving" in electromagnetic radiation? According to Maxwell, it is the strengths of the electric and magnetic fields as they travel through space. The two fields are oriented at right angles to each other and to the direction of travel. As the electric field changes, it induces a magnetic field, which then induces a new electric field, etc., allowing the wave to propagate itself through space. 'The difference between a Miracle and a Fact is exactly the difference between a mermaid and seal. It could not be expressed better.' -- Samuel "Mark Twain" Clemens |
| 08-12-2014 13:20 | |
| Abraham3 (256) |
peterlward wrote: This is wrong Mr Ward. It is basic physics that EMR waves can and do. Our description of the propagation of light through a vacuum ("Our" being Orogenicman, Surface Detail and me) may be found in any of a hundred different textbooks. Your description is what is missing here. We have yet to get from you how an oscillating, propagating signal can have a frequency but not a wavelength. If I put a 1 kHz tone out a speaker, I can say that the speaker cone has no wavelength because it isn't moving. I cannot say that about the sound waves produced. Please tell us how light can oscillate and propagate and yet not have a wavelength. Do you envision the entire beam of light oscillating in unison? Do you believe the field vectors of a beam of light are identical along its entire length? If so, you need to refresh yourself regarding special relativity. Nor have we heard from you why you seem to believe electric or magnetic fields require matter to exist. I am also very interested in hearing what happened to the warming that your theory says should have been produced by Laki Grímsvötn and perhaps even a better explanation of what caused the Earth's significant warming between 1910 and 1941. Edited on 08-12-2014 14:00 |
| 08-12-2014 18:13 | |
| peterlward★☆☆☆☆ (69) |
I readily admit that discovering that waves cannot exist in space is quite different from what most people think and what most textbooks say. But recognizing this has major implications for climate and for basic physics. The bonds holding matter together provide the restoring force required for wave motion. There are no bonds in space. Neither of you have been able to explain in actual, observable terms the physics of waves in space. I have explained frequency in space many times, but here is a draft section from the paper I am writing on the Physics of Global Warming: Thermal energy: The molecular bonds that hold matter together are not rigid. The length of each bond oscillates around a potential energy minimum between attractive electrostatic forces when atoms are close and repulsive electrostatic forces when atoms are too close [Anderson, 2009]. Both the frequencies and the amplitudes of these oscillations increase when matter is heated – typically increasing the volume [Planck, 1897]. Heated enough, the bonds come apart – solid matter melts. Cooled toward absolute zero, the amplitudes and frequencies of these oscillations approach zero, leading to the smallest volume and highest density configuration of any piece of matter. The lengths of these oscillating bonds are very small so that the frequencies of oscillation are typically very high. At room temperature, the frequency with the peak amplitude of oscillation is on the order of 30 terahertz (30 times 10^12 cycles per second) and the atoms and molecules are moving at velocities approaching one kilometer per second [Grossman, 2014]. Thermal energy in matter, the internal energy of matter, which we think of and measure as temperature, is simply a broad spectrum of frequencies of oscillation of the bonds that hold matter together. The heat capacity of matter, its ability to store thermal energy, increases with the number of degrees of freedom of these oscillations [Grossman, 2014]. A degree of freedom is often visualized as a spring holding two pieces of matter together. Thermal energy can be thought of as the constant exchange of potential energy and kinetic energy as these "springs" oscillate. In an ideal gas where there are no bonds, thermal energy is stored simply as the mean kinetic energy of translation of all atoms and molecules making up the gas. These oscillations, when on the surface of matter, induce in air or space, through the motion of charge, an oscillating electric field that induces an oscillating magnetic field that induces an oscillating electric field, and so on. The amplitudes and frequencies of oscillation on the surface of matter are propagated away from the surface as an electromagnetic field. Thermal energy in matter is radiated as electromagnetic energy through air and space. Maxwell proposed that the velocity of propagation of this electromagnetic field, what we call the speed of light, is equal to one over the square root of the electrical permittivity times the magnetic permeability, basically one over the smallest unit of time that it takes for an electric field to induce a magnetic field to begin to induce an electric field. The frequencies contained in electromagnetic radiation are well observed not to interact with each other and not to change over distance propagated, even galactic distances, except for Doppler effects where the emitter and receiver are moving relative to each other. The amplitudes, on the other hand decrease with the inverse square of the distance propagated because the amplitude spreads out over the surface of a sphere whose radius is the distance propagated. In 1900, Max Planck derived empirically an equation, now known as Planck's law, that approximates the observed spectrum of frequencies and amplitudes observed as a function of the temperature of the matter at thermal equilibrium. To derive this law, he found that he had to postulate that energy in radiation (E) equals frequency (ν, the Greek letter nu) times a constant (h), now known as the Planck constant. E= hν is used widely in photochemistry to designate the energy needed to cause a chemical reaction. For example: O2 + hv (λ<242.4 nm) → O(3P) + O(3P) which says the chemical bond of an oxygen molecule (O2) in the presence of solar radiation containing sufficient energy (hv) oscillates with high enough energy to overcome the bond energy, forming two oxygen atoms in the ground-level triplet state O(3P). The required energy (hv) has a frequency greater than 1.24x10^15 cycles per second which has an energy greater than 5.11 electron volts. Traditionally we express this energy as a wavelength (λ) of less than 242.4 nm (nanometers). While we are used to calculating wavelength as the velocity of light divided by the frequency, wavelength is a mathematical number, not a physical one. Waves of electromagnetic radiation cannot physically occur in space because waves deform the bonds holding matter together and there are no matter and no bonds in space. It was proven in the late 19th century that there is no "luminiferous aether" in which waves of light can travel. Frequency, on the other hand, physically exists in space, is the form in which thermal energy is radiated, and can be measured. Note that energy (E=hν) is not a function of amplitude or brightness. This is a very difficult reality to become comfortable with because we are used to thinking that if we have more radiation, then we have more energy. This assumption is fundamental to how we calculate radiative forcing in climatology. For waves in matter, energy is proportional to the square of the amplitude, but for radiation in space, energy is a function of frequency and amplitude (brightness) simply specifies the amplitude of the oscillation on the surface of the matter that induced the oscillation divided by the square of the distance propagated. There is much to add to this including a plot and discussion of Planck's law, but there is the basics of the physics. I encourage you to try to move science forward rather than think you can prove me wrong based on your current limited understanding. As for Laki, I explained that there were 10 eruptive phases of Laki that formed aerosols in the lower stratosphere causing cooling. Aerosols usually win out, are more thermally effective,than basic ozone depletion. The details of the Laki eruption are very interesting and by no means simple. There is amazingly good documentation for that many years ago but it is limited in geographic extent. I wish to keep you focused on the physics of EMR in space and so will not expand on this yet. |
| 09-12-2014 01:09 | |
| peterlward★☆☆☆☆ (69) |
Reviewing my notes: Mt. Asama in Japan erupted from May 9, 1783 with the climactic eruption beginning on August 4 and lasting for 15 hours. This was a huge plinian eruption with andesitic pumice falls, pyroclastic flows, etc. and certainly produced a major aerosol and associated global cooling. Laki began erupting June 8, 1783, and lasted until at least October 25th. Some aerosols were noted related to Laki, but sorting out the simultaneous effects of Asama is not easy. The Spannagel Cave d18O proxy for temperature data, one of the best records of global temperatures for the past 9000 years, show that the greatest low of the Little Ice Age was around 1758 and that the Laki and Asama eruptions occurred during the rapid warming out of the third lowest temperatures of the Little Ice Age. You have to be very careful drawing any simple conclusions about cause and effect from these data. Orogenicman: Your dismissal of the up to 3.3oC warming of Europe during July, 1783, (Figure 8 of Thordarson and Self, 2003) is quite unscientific. The observed warming was close to the period of time when the "dry fog" hung over Europe. The cause of this warming is not obvious, but it is related to the eruption of Laki. |
| 09-12-2014 03:43 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
peterlward wrote: I agree that one has "to be very careful drawing any simple conclusions about cause and effect from these data". Thordarson and Self, 2003, certainly were when they pointed out on page 18 (see my earlier reference to this page)" The July anomaly is strongest in western Europe and declines gradually with increasing distance from Laki, which can be taken as support for the above hypothesis. However, it is challenged by the fact that at the same time cool conditions prevailed in Iceland and Faeroe Islands [Ho´ lm, 1784; Jo´nsson and Pa´ lsdo´ ttir, 1992; Lievog, 1783], regions which were consistently exposed to the gaseous emissions from Laki. Also, unusually warm temperatures are not seen in the August temperature records from the same European stations although the sulfuric haze was still present in abundance [Thordarson, 1995]. An alternative explanation is that the warm spell may have been caused by somewhat unusual developments in the atmospheric circulation pattern over Europe in July 1783. I might also point out that according to this paper: http://tinyurl.com/lvq8tb8 Assessing the climatic impact of the A,D. 1783 eruption of Mt, Asama, Japan, is complicated by the concurrent eruption of Laki, Iceland. Estimates of the stratospheric loading of H2SO4 for the A .D. 1108 eruption of Asama derived from the SO42 time series in the GISP2 Greenland ice core indicate a loading of about 10.4 Tg H2SO 4 with a resulting stratospheric optical depth of 0,087. Assuming sulfur emissions from the 1783 eruption were only one-third of the 1108 event yields a H2SO4 loading value of 3.5 Tg and a stratospheric optical depth of only 0.029. These results suggest minimal climatic effects in the Northern Hemisphere from the 1783 Asama eruption, thus any volcanically-induced cooling in the mid-1780s is probably due to the Laki eruption. 'The difference between a Miracle and a Fact is exactly the difference between a mermaid and seal. It could not be expressed better.' -- Samuel "Mark Twain" Clemens Edited on 09-12-2014 03:54 |
| 10-12-2014 01:08 | |
| Abraham3 (256) |
peterlward wrote: It is completely contrary to what ALL textbooks say. Given that every physicist for almost the last century would disagree with you, given that this is not your native field, given that your efforts have been solitary and at least to some extent casual, I think it's a bit premature to say that you have yet done any "discovering". You have a hypothesis. peterlward wrote: That is a major understatement. You would overturn Einstein and every single physicist since. You're attempting to refute quantum mechanics. peterlward wrote: For mechanical waves, yes. For EMR, no. peterlward wrote: There are some, they're just further apart. But the point is irrelevant because electric and magnetic fields do not require matter to propagate. We have said this to you repeatedly but you make no response. Can you please acknowledge this point. EMR travels through matter and is produced by matter by changes in the energy state levels of the atoms and molecules themselves, NOT by any deformation of the intramolecular bonds. peterlward wrote: Consult ANY textbook on the topic. All three of us have given you essentially the same explanation that you have given back to us. Oscillating, crossed electric and magnetic fields, propagating at c. peterlward wrote: You tell us that light has a frequency because we see it and because Planck empirically found a relationship. That does not explain why you think EMR needs matter and does not explain why you think EMR can propagate and oscillate and not have a wavelength. EMR is not a mechanical wave. While its absorption and emission from matter does cause physical changes in atomic structure, those are NOT changes in intramolecular bonds, they are not synchronous and do not form or represent wave fronts. peterlward wrote: This is a lovely discussion of the kinetic theory of heat. Unfortunately, that has nothing to do with the transmission of EMR through matter or the vacuum. Heat conducting through a solid is not EMR. peterlward wrote: In the time between the electric field or the magnetic field reaching a peak potential and that field reaching that same peak again, the radiation has moved (c / 30e9 Hz) meters away. That distance is one wavelength of 30 terahertz radiation. peterlward wrote: And he was correct. peterlward wrote:The frequencies contained in electromagnetic radiation are well observed not to interact with each other What do you mean here Mr Ward? EM radiations may be combined by amplitude, frequency and phase modulation. And as far as crossing wavetrains go, they will behave precisely like mechanical waves. The field at any point will be the vector sum of all the passing waves. When the passage is complete, the waves will show no effect. peterlward wrote: Redshift from the expansion of space is not, strictly speaking, due to motion of the emitter or receiver. And it presents a problem for your theory. How does either form of Doppler take place if the signal has no wavelength? Why is the frequency affected by either the relative motion of the transmitter and receiver or by the stretch of space if there is no wave to be lengthened? peterlward wrote: Yes. You provided that as an explanation for the different radiant intensities of our sun and a drop of hot wax. peterlward wrote: As you've been told several times before, the Planck-Einstein relation concerns the energy IN A PHOTON, not in all radiation. From Wikipedia:
peterlward wrote: Almost. What your chemical equation is actually saying is that after absorbing a PHOTON with a wavelength less than 242.4 nm, a single molecule of diatomic oxygen will disassociate. peterlward wrote: I'm afraid it's precisely the opposite. An EM wavelength has a fixed length, no matter what units one uses. The frequency of EM radiation - of any oscillating signal - is dependent on a completely arbitrary length of time that one applies to the expression; the frequency per year is much higher than the frequency per second. The only way to fix it is to use the same arbitrary time period to quantify the signal's velocity. And then what do you actually have? You have how many oscillations will fit in a given distance. What's another name for that value? Wavelength. peterlward wrote: Your previous descriptions of heat in a solid and of the propagation of mechanical waves simply do not establish or even support this claim. This is a completely unsubstantiated assertion. EMR does NOT deform the intramolecular bonds of matter. Heat in a solid is NOT EMR. peterlward wrote: Not quite. It was proven in the late 19th century that there is no "luminiferous aether" in which light could travel. Yet travel it does. The PROPER conclusion? Light does not require a medium. peterlward wrote: Wavelength can be directly measured, both here and in space. Interferometry is the most direct method I can think of and it has and will be used in space. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interferometry and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_Interferometry_Mission peterlward wrote: The energy in that relation isn't such a function because it describes the energy in a single photon which has neither amplitude or brightness. peterlward wrote: Mr Ward, please look up your own sources regarding the Planck-Einstein relation. You will find that just as in the Wikipedia text above, it clearly states that this equation tells us the energy content of a single "charged atomic oscillator". If you plug in the frequency of any particular EM radiation, the Energy value you will get is infinitesimally small. The value of the Planck constant is 6.62606957(29)×10-34 Js or 4.135667516(91)×10-15 eVs. You seem to be saying that the entire output of our sun would not provide enough energy to warm a cup of tea. If you have more photons, you DO have more energy. peterlward wrote: Which assumption? Planck's and Einstein's or yours? peterlward wrote: The energy of EMR traveling through matter, gaseous, liquid or solid (ex: air, water, glass), is NOT given by the amplitude of any physical motion of its molecules. And after telling us repeatedly that the energy of EMR is dependent only on frequency, you now include amplitude. Can I ask why the change? peterlward wrote: That is NOT the basics of the physics. The physics says that EMR propagates through space and transparent types of matter as oscillating, crossed electric and magnetic fields, which have frequencies and wavelengths. Light does NOT require matter to propagate and it's propagation through matter is NOT by means of a mechanical wave. peterlward wrote: I am not a scientist. I am an engineer. My "research" on AGW consists of reading the literature. There are thousands of folks out there who know these topics better than do I, who do research for a living and have been doing so for years. I am prone to take their word. A logical appeal to authority is valid if the authorities referenced actually are experts in the field and if there exists a genuine consensus on the subject in question. That condition is more than satisfied on the issue of greenhouse warming and human responsibility for the warming observed in the 20th and 21st centuries. That condition is FAR more than satisfied on the "issue" of the propagation of light. You are attempting to claim nearly a century's worth of physics incorrect in a field which is NOT your specialty. I do not believe either the level of evidence you've collected or your understanding of the fundamental physics describing the propagation of EMR are sufficient to make such a challenge. peterlward wrote: Laki's eruptions consisted of phreatomagmatic explosions only for the first few days of what would be an 8 month long eruption. The bulk of the enormous amount of SO2 released was NOT thrown into the stratosphere. If any eruption in the last milennia would have demonstrated the warming you claim diffusive eruptions cause, it should have been this one. If the warming from it's 8 month eruption can be canceled by the aerosol cooling effects of a 15 hour eruption, your theory has problems. You should realize that you will need an exceptional record of diffusive volcanoes to explain the extreme rate of warming between 1910 and 1941. Be that as it may, I will leave the vulcanism comments to Orogenicman. Edited on 10-12-2014 01:53 |
| 10-12-2014 21:12 | |
| peterlward★☆☆☆☆ (69) |
Gentlemen, You have had the unique opportunity to discuss climate research on the frontier of science because Jeppe Branner, who may very well be one of you, invited me to post a message on this website on November 18 in response to my press releases. You have attacked this initial message extensively before you even bothered to look at the video or read the website in an effort to understand the scientific basis for what I am saying. You have not been very professional in many of your posts, which explains in part why this website is not overloaded with professional climatologists. You seem to think that your opinions are valued and are sufficient to prove me wrong. This is Science and the value of your opinions depends on the depth of your thought, the extent of your knowledge, and the scientific arguments that you can muster. And that takes more work than you have apparently spent on this discussion to date. You are correct to question my claim that EMR in space is frequency. This is a major break from the past with profound implications for climatology and basic physics. But saying that I am wrong simply because of what all the old papers and textbooks say is nothing new. I have worried about my divergence from "common knowledge" for many years and I am now prepared to defend my position to the best scientists on the planet. Physics has been obsessed with wavelength at least since Maxwell's time. But the physical evidence for thermal energy being oscillations in matter and space is overwhelming. I have seen this because I have very seriously questioned several things that others take for granted and because as a geophysicist, I have not been steeped in traditional mathematical physics. Just because certain mathematics makes the right predictions to 13 decimal places, does not prove that the assumptions behind that mathematics are physically correct. And I am a stickler for evidence of physical reality. Physics should be about physical reality, what is actually going on. In the early 1900s, physicists decided that quantum mechanics did not have to make physical sense. That was a bad choice. You do not wish to accept the evidence that I have very carefully laid out and I simply do not have the time to continue to hold your hands to get you to do the science. My nearly 50 posts have basically been a huge waste of time. I have stuck with it to see if you might come up with something that I need to think seriously about. But you have not come close. I do appreciate Abraham3's discovery of a confusion between the Euler number, which is a constant, and the Euler Constant. I will be very surprised if more such tweaks are not needed as people spend time studying my website. But I will also be very surprised if anyone can come up with any serious reasons to doubt my primary conclusions that thermal energy in matter and space is contained in the frequency, that increases in UV-B reaching Earth when ozone is depleted is the primary cause of global warming, and that greenhouse-gas theory is based on several assumptions that are simply not correct. Laki is a complex eruption with clear evidence that some stratospheric aerosols were formed and these usually cause cooling that is globally more important than the warming caused by ozone depletion. The warming in July is contemporaneous with the dense, dry fog containing unusually high levels of SO2. SO2 absorbs heavily in the visible and UV ranges, providing a potential explanation for the 3oC warming observed. You cannot just dip into the extensive literature and pluck sentences that happen to agree with you. I stand by the description of Laki on my website, and the distinction between effusive volcanoes that do not form aerosols and explosive volcanoes that do, but that is just the tip of the proverbial iceberg. I have a poster to prepare for next week at the AGU meetings, another in early January for the AMS meetings, a paper to finish and two short videos to prepare. I am sorry, but I cannot continue this drain on my time and am discontinuing subscription to this thread. Best wishes, Peter |
| 10-12-2014 22:21 | |
| Surface Detail★★★★☆ (1673) |
What an extraordinarily deluded man Mr. Ward is! I don't think I've ever witnessed such an eloquent combination of hubris and incomprehension on the internet as his. How could anyone seriously claim that the entirely of quantum physics is misguided while simultaneously displaying such a rudimentary understanding of the topic? Incredible. As a matter of fact, I did read some of his website. While I'm not sufficiently knowledgeable in atmospheric chemistry or vulcanology to be able to comment on those areas, I do have a PhD in plasma physics and hence some knowledge of radiative processes. So it quickly became clear to me that the parts of his website concerning radiative transfer of energy are basically gibberish, and I have to admit that I did laugh out loud when I read his nonsense about quantum entanglement of photons, something that he plainly has no understanding of whatsoever. Many thanks to my fellow defenders of science, especially Abraham3, for all the work you've put in to patiently repudiate Mr. Ward's assertions. It's very important that this kind of pseudoscientific blather is shown up for what it really is, lest it be taken seriously by people without a scientific background and used to further delay any action towards reducing human emissions of greenhouse gases. Hopefully your wife will forgive you for the hours spent at the computer! Edited on 10-12-2014 22:24 |
| 11-12-2014 06:51 | |
| Abraham3 (256) |
Thanks, but I wish I'd been able to keep my tongue a bit more in check. Dr Ward is a distinguished geophysicist in the field of vulcanology and deserves better than the treatment the internet would give him. I wish it were possible to disagree with someone's technical views without the implication of disrespect. Perhaps it's possible somewhere, somehow, but it seems to be beyond me at the moment. I know he's actually been treated with greater deference and professionalism here than he would anywhere else I'm familiar with, but I probably have a tendency to frequent dives. But he obviously hasn't been hanging out in such places. I trust the AGU will give him the respect he has earned over the years. Dr Ward, I hope your AGU presentation comes off well |
| 11-12-2014 14:05 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
I would agree with both of you gentlemen, and I too wish him well with his presentation at the AGU. Having said that, I tend to think that it won't receive the accolades he is hoping for. What struck me the most was his insistence that care be taken not to make hasty conclusions about data while simultaneous making the hasty conclusion with regard to the a possible connection between short period of warming that occurred in the Netherlands in August 1873 and the Laki eruption, when the very paper he referenced stated emphatically that any connection to the event was dubious, at best. |
| 11-12-2014 14:11 | |
| Abraham3 (256) |
Yup... |
| 11-12-2014 18:22 | |
| orogenicman★☆☆☆☆ (57) |
orogenicman wrote: Correction. That should read July, 1873. My bad. 'The difference between a Miracle and a Fact is exactly the difference between a mermaid and seal. It could not be expressed better.' -- Samuel "Mark Twain" Clemens |
Join the debate Global warming is caused by ozone depletion, not greenhouse gases:
Related content
| Threads | Replies | Last post |
| The "radiative Greenhouse effect" does not exist | 140 | 15-04-2024 19:43 |
| 'Greenhouse' Effect? | 49 | 30-11-2023 06:45 |
| The SCIENCE of the "Greenhouse Effect" | 291 | 05-11-2023 22:46 |
| How covid 19 vaccine caused Jamie Foxx to become blind and paralyzed | 2 | 08-06-2023 03:23 |
| Nitrate Reduction - Powerful Greenhouse Gas Emission AND Alkalinity | 102 | 05-06-2023 13:19 |